ELISA elaborate as Enzyme Immuno Assays/Enzyme Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay.
These two terms go synonymous with each other with little modification in the test system.
ELISAs finds an enormous utility in the field of immuno diagnostics and are immuno chemical methods for the determination of anlytes such as
v Proteins/Peptides
v Bacterial and viral antigens and their specific antibodies,
v Hormones
The crucial element of detection is an antigen and antibody interaction (immune complex).
The immune complexes are detected and measured by means of an enzyme label that is conjugated to appropriate biomolecules.
EIA/ELISA
The enzyme activity is detected by means of a specific substrate
In the subsequent steps Substrate yields a colour
The intensity of colour can be measured in photometer.
The intensity of colour is proportional to the analyte concentration in serum.
ELISA makes use of Microtitre plates
Ø which are made up of polystyrene
Ø On to which biomolecules are passively or covalently absorbed.
ELISA as screening test……..
ELISAs are preferred screening tests in the detection and diagnosis of most of the infectious diseases because of their
ü Speed
ü Sensitivity
ü Specificity
ü Selectivity and
ü Simplicity to perform.
ELISAs do not involve any hazardous radioactive material and are safe to perform.
Enzyme labels used in ELISA
Compounds used for labeling biomolecules:
ELISA Categories
- Direct ELISA
- Indirect ELISA
- Competitive ELISA
- Noncompetitive (Sandwich ELISAs)
1. Direct ELISA
Antigen/Antibody is passively absorbed on to the solid surface (polystyrene).
The immobilized antigen/antibody is allowed to react directly with the enzyme labeled antibody/antigen.
A colour is developed by using a specific substrate
The intensity of colour measures the antigen and antibody interaction qualitatively.
Utility of Direct ELISAs
These types of ELISAs do not have commercial utilities and are used only for practical identification of either antigen or antibodies at the laboratory level.
2. Indirect ELISA
Synonymously termed as classic EIAs or antiglobulin immunoassays.
Generally used for the detection of antibodies by using a antiglobulin conjugated to enzyme labels in a two step reaction.
Anti-immunoglobulin enzyme conjugate used may be
Ø Anti IgG
Ø Anti IgM
Ø Anti IgA
is used as a detector.
Basic ELISA protocol (Indirect ELISA)
- Bacterial/viral antigens are coated onto the microwell or polystyrene beads.
- Block non-specific binding sites with non ionic detergent or BSA, skimmed milk powder, casein. (choose the blocking agent whichever avoids non specific interactions)
- Add diluted sample and incubate
- Wash off unbound material by using a washing buffer with non-ionic detergent.
- Add enzyme labeled anti-human immunoglobulin (anti IgG, IgM, IgA as the case may be) enzyme conjugate and incubate.
- Wash off unbound material.
- Add enzyme specific substrate and incubate in dark.
- Stop the reaction and read the absorbance in a photometer.
- The intensity of colour change is proportional to the antibody concentration present in the specimen
Indirect ELISA

ELISA range from under Indirect (Classic) ELISA…………………..
CMV IgGCMV IgMDengue IgGDengue IgMEBV IgGEBV IgMH. pylori IgGH. pylori IgA,Rubella IgGRubella IgMToxo IgGToxo IgMVZV IgMAnti-HCVHIV 1+2HSV 1 IgGHSV 2 IgGHSV IgMMeasles IgGMeasles IgMMumps IgGMumps IgMVZV IgG
3. Competitive ELISA
In competitive formats unlabeled analyte (usually antigens) in the test sample is measured by its ability to compete with enzyme labeled antigen to bind with specific antibodies that are immobilized on the solid surface.
The undiluted test serum, which contains antigen and the enzyme labeled specific antigen conjugate, are added together for the competition to occur to bind to the passively absorbed antibody.
The unlabeled antigen (analyte) blocks the antigen binding sites of antibody that is passively absorbed on to the solid surface thus not allowing enzyme labeled antigen (conjugate) to bind to the antibodies resulting in very less colour upon addition of substrate.
The sample, which do not contain antigen, will allow the binding of labeled enzyme antigen conjugate to antibody thus gives intense colour upon addition of substrate.
An intense colour signifies a non reactive sample while lack of colour signifies a reactive sample thus indicates the intensity of colour is indirectly proportional to the analyte concentration in the sample.
Excellent ELISA range from HUMAN under Competitive ELISA…………………..
Since the sample and conjugate are added together and incubated competitive ELISAs take less time to perform.
Used widely in the detection, determination and quantification of
Ø Thyroid hormones (T3, T4, fT3, fT4)
Ø Steroids like Cortisol, DHEA-S (Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulphate), Estradiol, Estriol, Progesterone, Testosterone.
Ø Drugs of Abuse.
4. Non competitive (Sandwich ELISA)
Analyte is sandwiched between two homologous antigens or antibodies -one is passively absorbed on to the solid surface and the other is conjugated to an enzyme.
Classified into
Ø Double Antibody Sandwich Assay.
Ø Double Antigen Sandwich Assay.
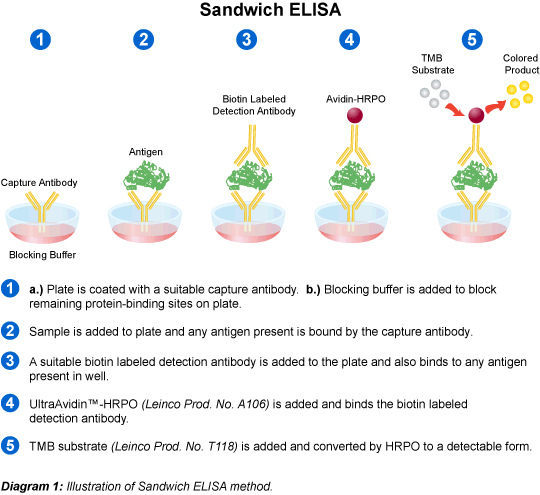

The intensity of colour is directly proportional to the concentration of analyte present in the specimen and can be represented by a dose response curve.
Utilities of Double Antibody Sandwich ELISAs………..
Sandwich ELISAs are instrumental in detecting critical analytes such as
Ø Cardiac markers (Troponin I, Troponin T, Myoglobin, CK-MB)
Ø Hepatitis markers (HBsAg)
Ø Hormones (FSH, TSH, HCG, LH, Prolactin)
Ø Cancer markers (AFP, CEA, PSA)
Ø Total IgE
Utilities of Double Antigen Sandwich ELISAs………..
Classic example for double antigen sandwich ELISAs is for the detection and diagnosis of HIV specific antibodies in the serum specimen.
This type of ELISAs are termed as third generation ELISAs wherein all types of antibodies (IgM, IgG and IgA) are detected.
These ELISAs are much preferred over indirect ELISAs as these are very sensitive to detect the disease in the early seroconversion period.
Detects all antibodies because of the specific antigens used both in solid surface and in the enzyme conjugate (detector).
No comments:
Post a Comment